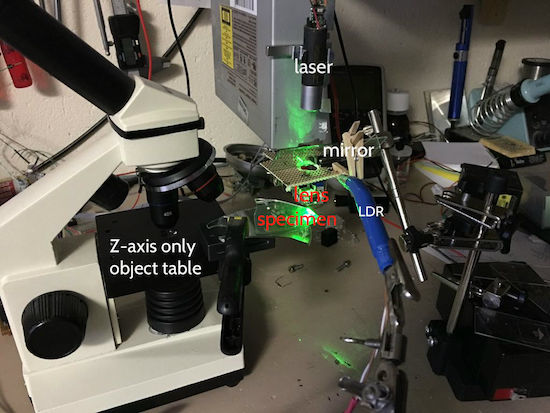
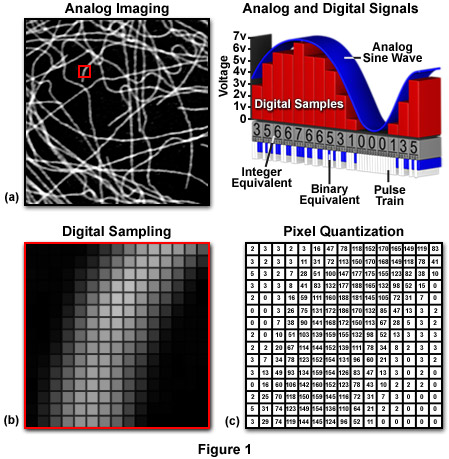
Relatively thick specimens can be imaged in successive volumes by acquiring a series of sections along the optical z axis of the microscope.
Laser scanning microscope magnification.
A the use of microscopy to observe and investigate different types of cell and cell structure in a range of eukaryotic organisms to include an appreciation of the images produced by a range of microscopes.
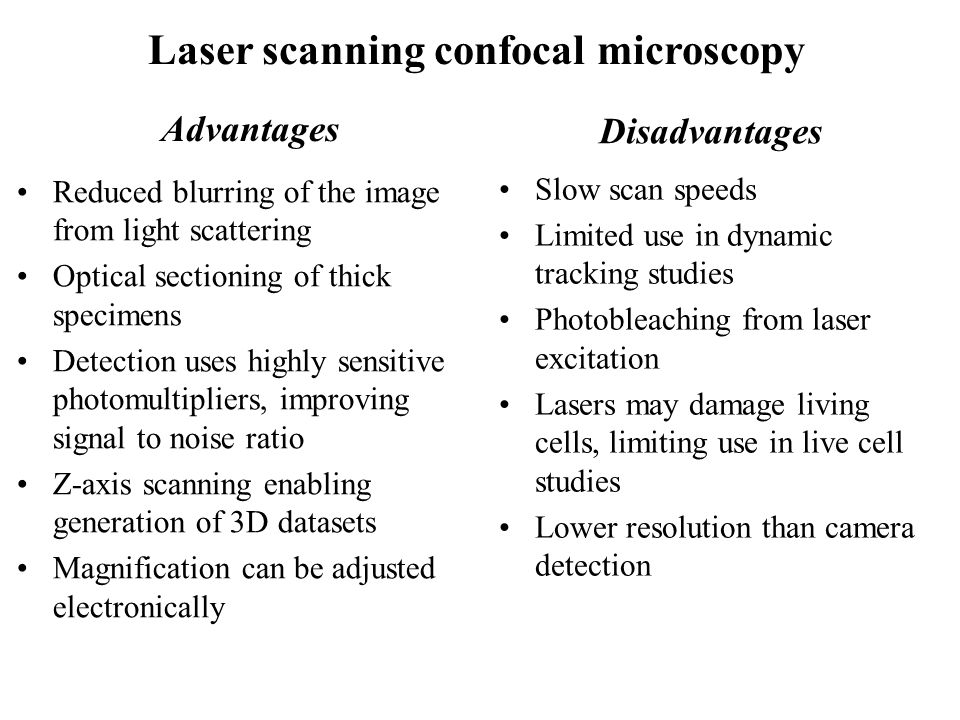
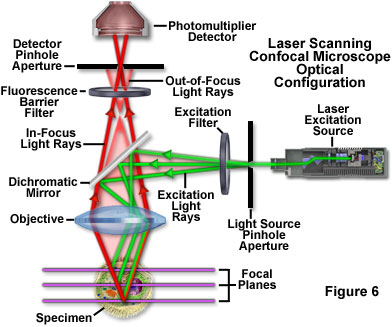
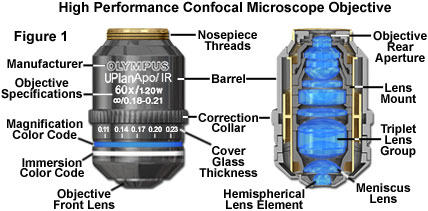
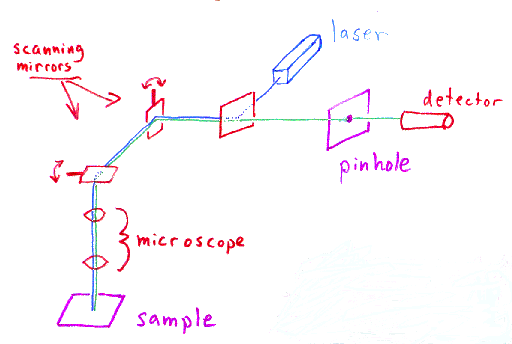
Laser scanning confocal microscopy laser scanning confocal microscopes employ a pair of pinhole apertures to limit the specimen focal plane to a confined volume approximately a micron in size.
Clsm combines high resolution optical imaging with depth selectivity which allows us to do optical sectioning.
The confocal laser scanning microscope clsm is a microscope which focuses only on a single focal plane and the unfocused plane will not be visualized.
Confocal microscopy most frequently confocal laser scanning microscopy clsm or laser confocal scanning microscopy lcsm is an optical imaging technique for increasing optical resolution and contrast of a micrograph by means of using a spatial pinhole to block out of focus light in image formation.
This technique captures the surface image and enables magnification control by reducing the scan area to smaller sizes thus increasing magnification without any resolution loss.
The confocal laser scanning microscope s aim was not to further increase magnification but to make clearer.
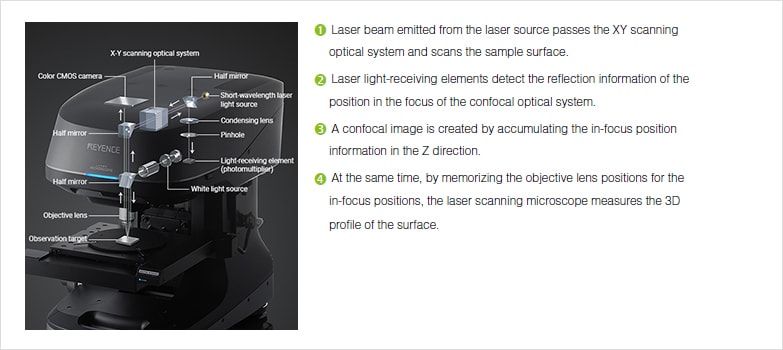
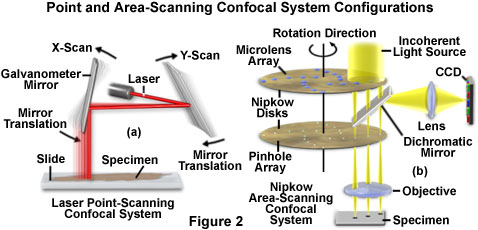
The laser scanning microscope uses a scanning design called beam scanning where the laser image path is scanned in a raster pattern on the surface of the sample.
With confocal laser scanning microscopy clsm we can find out even more.
Light microscope transmission electron microscope scanning electron microscope and laser scanning confocal microscope.
Expired practical laser scanning confocal microscope designs were translated into working instruments by several investigators.
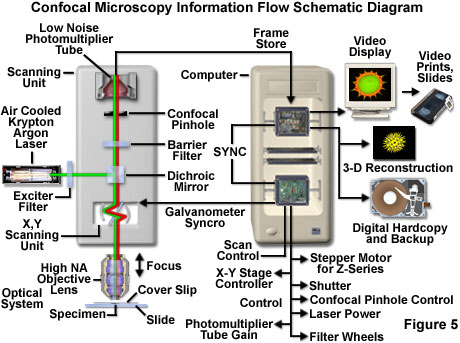
Capturing multiple two dimensional images at different depths in a sample enables the.
The laser scans across the object and an image is built up pixel by pixel on a screen.
In the past the traditional laser microscope excited the whole thickness of the sample resulting in saturated blurry images and sometimes visualizing false colocalization images.
.jpg?rev=33A9)