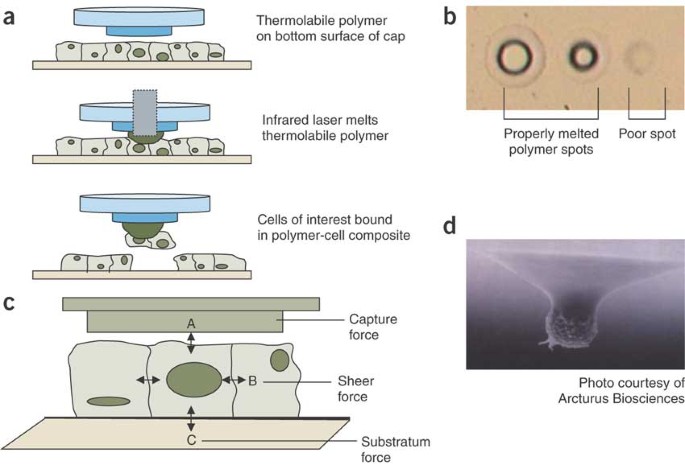
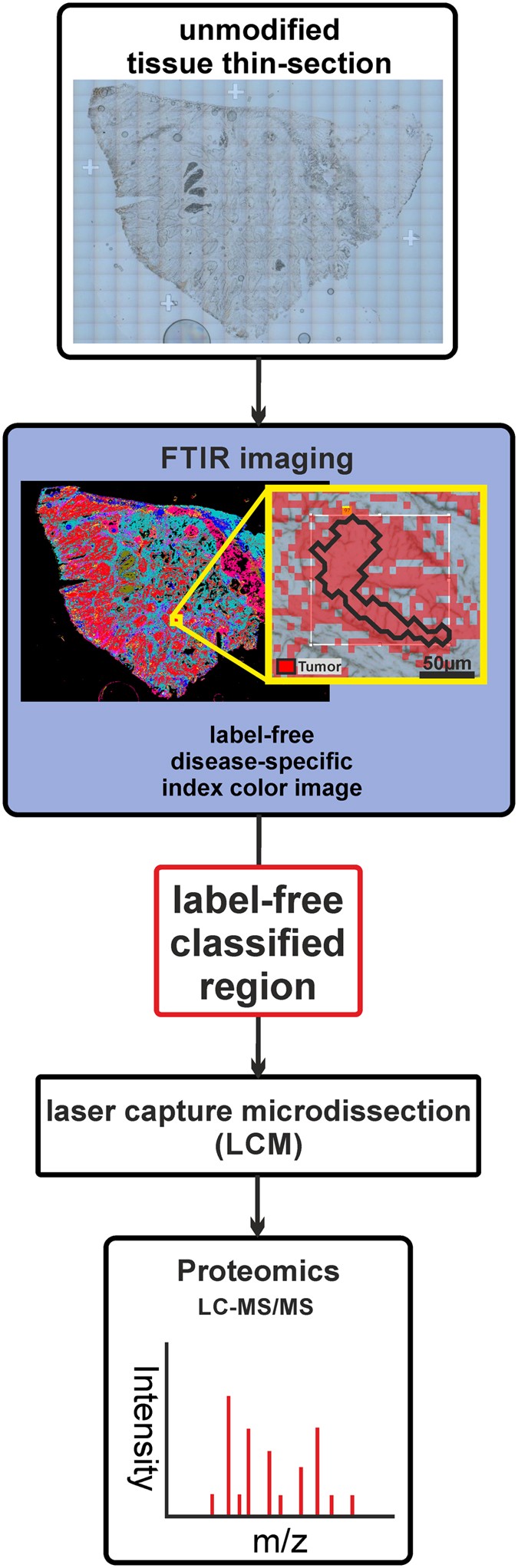
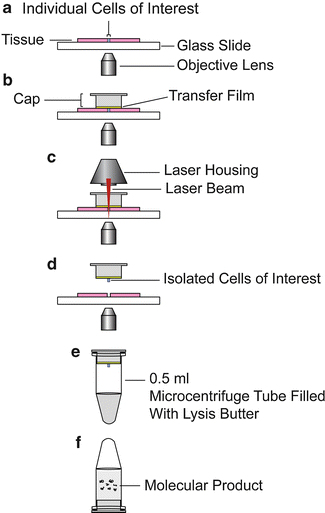
As opposed to xmd standard laser capture microdissection lcm is based on visual identification of target cells through a microscope 1 2.
Laser capture microdissection nature protocols.
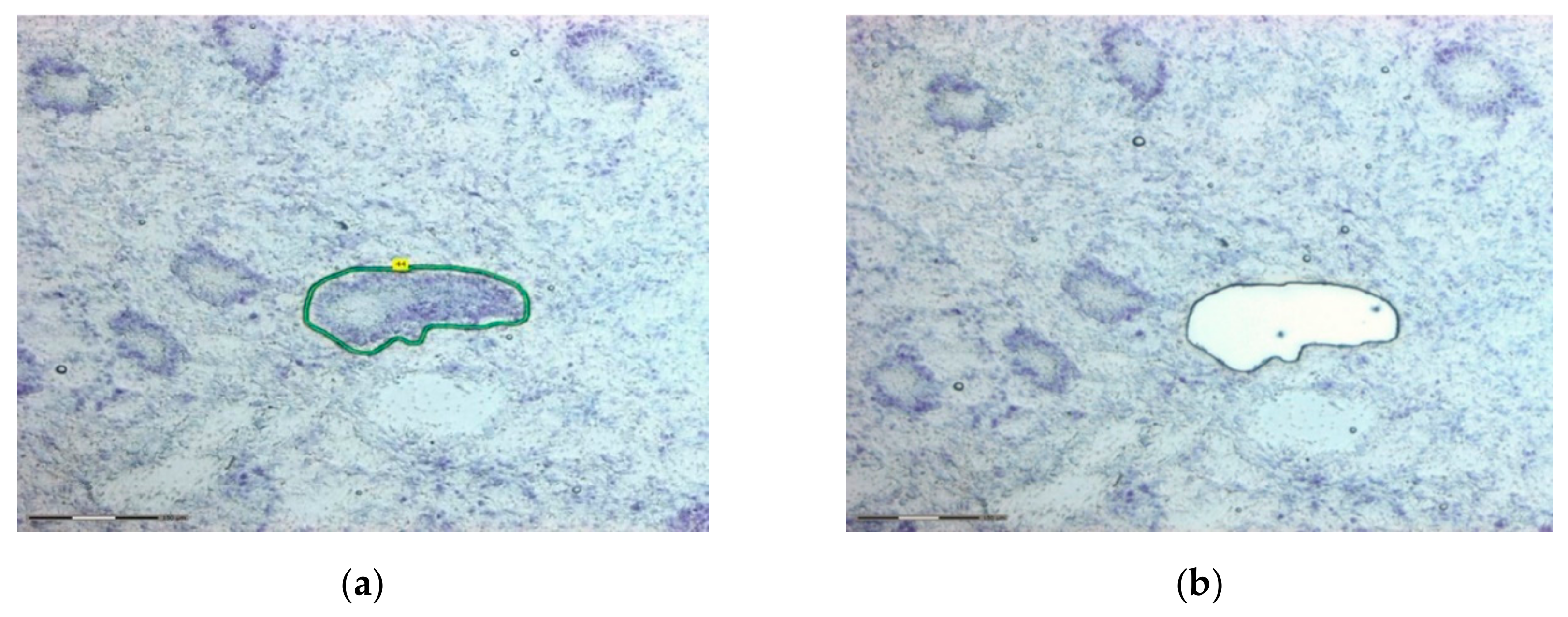
A histological section is stained and then a.
However there are no reproducible protocols to study rna in the brainand particularly in the substantia nigra.
Springer nature is developing a new tool to find and evaluate protocols.
Placenta 25 758 762 2004.
Laser capture microdissection is used to isolate single cells and amplified cdna.
Cite this protocol as.
2011 laser capture microdissection.
Decarlo k emley a dadzie o e mahalingam m.
Methods and protocols third edition seeks to aid researchers generally and pathologists in particular in moving their studies forward with these vital techniques.
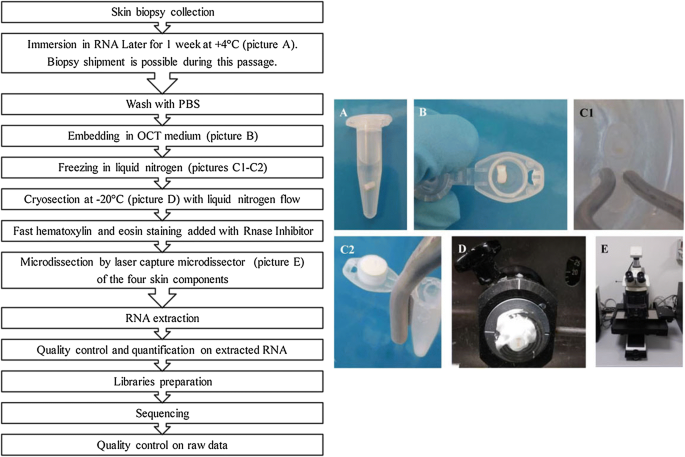
Laser capture microdissection lcm technology allows isolating zonal homogenous cell populations and consequently generating more accurate molecular and genetic data but the challenges during tissue preparation and microdissection procedures are to obtain acceptable tissue section morphology that allows histological identification of the desirable cell type and to minimize rna degradation.
This protocol enables amplification of the total transcript of a single prokaryotic cell for in depth analysis.
Laser capture microdissection lcm is a method to procure subpopulations of tissue cells under direct microscopic visualization.
Laser capture microdissection lcm allows the isolation of specific cellpopulations from complex tissues that can be then used for gene expressionstudies.
Laser capture microscopy lcm coupled with global transcriptome profiling could enable precise analyses of cell populations without the need for tissue dissociation but has so far required.
Eds laser capture microdissection.
Laser capture microdissection lcm offers a rapid and precise method of isolating and removing specified cells from complex tissues for subsequent analysis of their rna dna or protein content thereby allowing assessment of the role of the cell type in the normal physiologic or disease process being studied.